Can You Charge A Solar Panel With An LED Light?
Home – Info Center – Blogs –
Can You Charge A Solar Panel With An LED Light?

By Michael Zhang || Updated on 27th April 2024
Michael Zhang is a seasoned professional with 15 years of experience in the solar lights industry. Throughout his career, he has been actively involved in product design and developing, gaining valuable expertise and insight into the industry. Known for his dedication and professionalism, Michael has contributed significantly to the growth and success of various solar lights projects. His extensive knowledge and hands-on experience make him a trusted authority in the field, and he continues to innovate and excel in his role.
The biggest problem with solar lights is that they can’t get power on rainy days and can’t maintain normal operation. So some customers often ask us: Can indoor LED bulbs be charged by solar lights? Maybe we all expect the answer to this question is “YES”, but unfortunately, the answer is “Hardly”, next let’s explore the reasons.
Table of Contents
How Does Solar Panel Work?
How Does Solar Panel Work?
The sun emits energy in the form of waves that vary in length, from short ultraviolet waves to long infrared waves, and when sunlight shines, these waves move toward the Earth and hit the surface of solar panels.
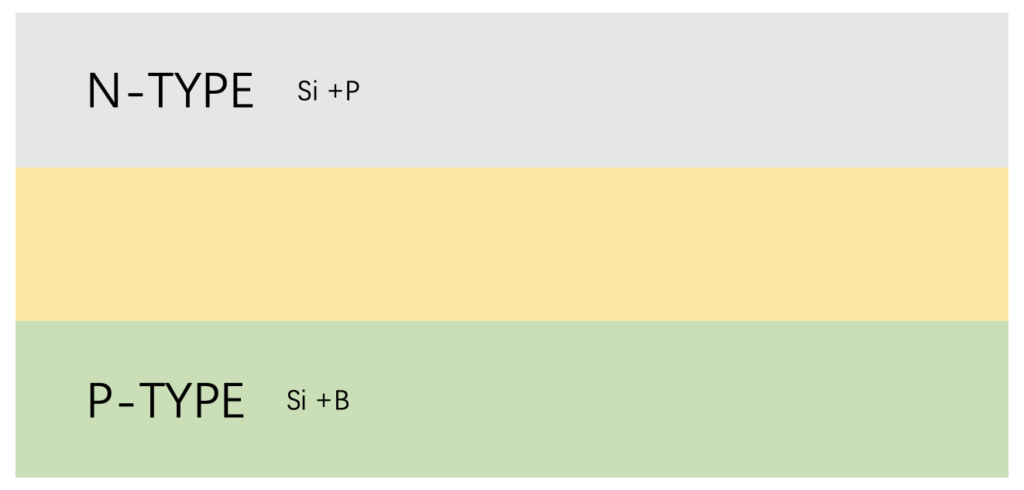
In fact, solar cells are composed of three layers. The top layer is silicon and a very small amount of elements that have more electrons than silicon, such as phosphorus. This allows excess electrons in the top layer to move freely, making the material more conductive. Therefore, the top layer is also called the negative electrode or N layer; the bottom layer contains silicon and elements with fewer electrons than silicon, such as boron, which reduces the number of mobile electrons in the bottom layer, thereby reducing the material’s conductivity to electrons. A missing electrons can be described as an effective positive charge, so the bottom layer is also called the positive electrode or P layer.
Explanation Of Two Solar Panel Batteries?
When light irradiates the surface of a silicon solar panel, the absorbed light waves knock the electrons in the middle layer off the silicon atoms, causing the electrons to loosen and leaving a positively charged area in the original area of the electrons, and then the loose electrons moving toward the top N layer, this layer is easy to accept electrons; at the same time, the loose positive charges move toward the bottom, reaching the bottom P layer. This layer is more accepting of positive charges. This will continue as long as there is sunlight.
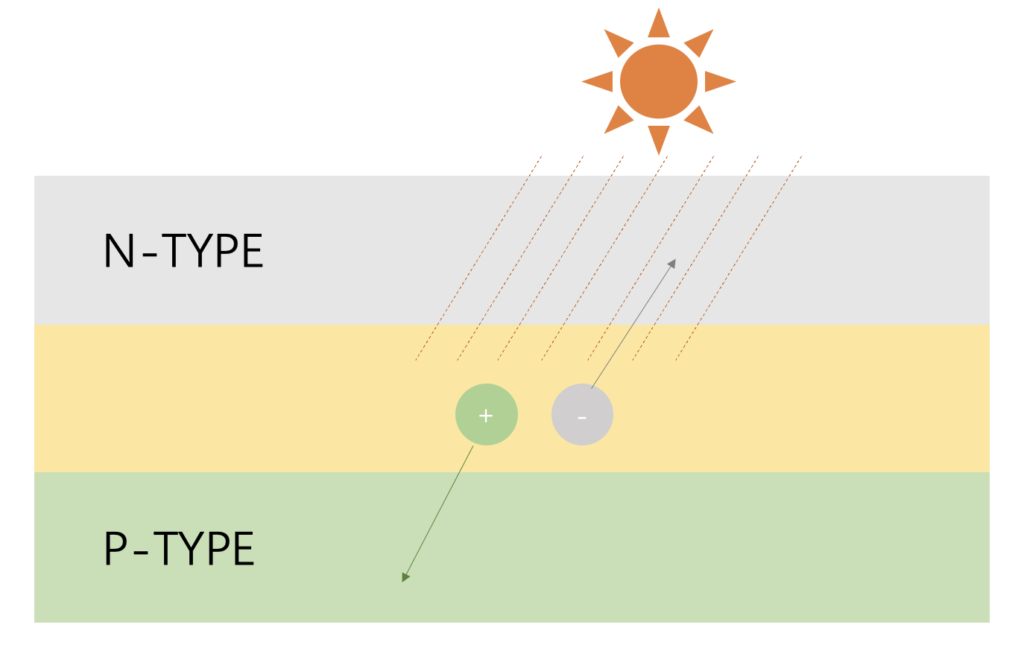
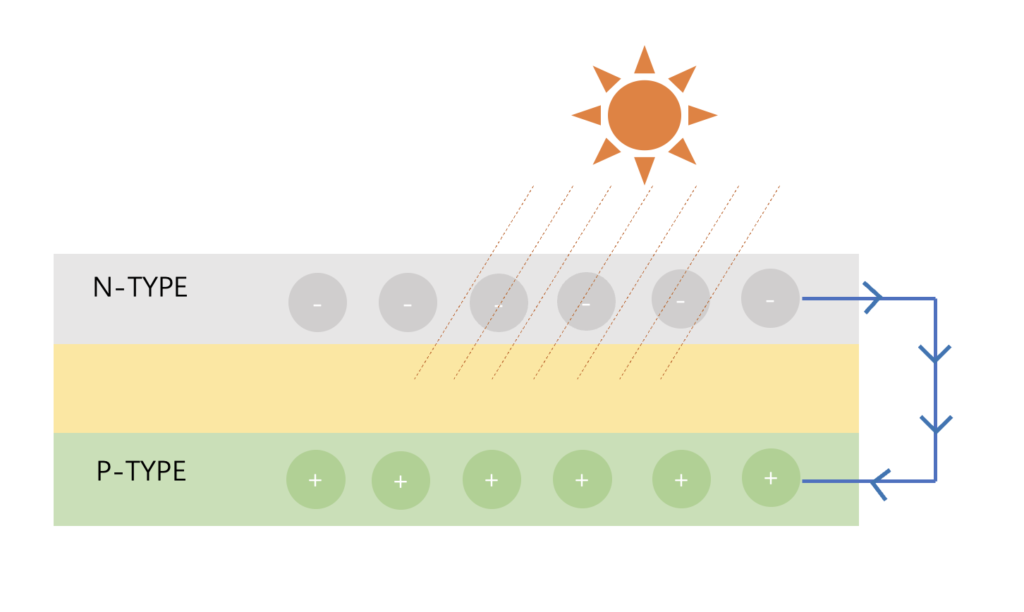
At this time, if a wire is connected between the top and bottom, a channel is formed for electrons to move from the N layer to the P layer, then a current is formed.
What Wavelength Do Solar Panels Use?
We have just mentioned that only absorbed light waves can knock down electrons in the middle layer. So what wavelengths of light can be absorbed by solar panels?
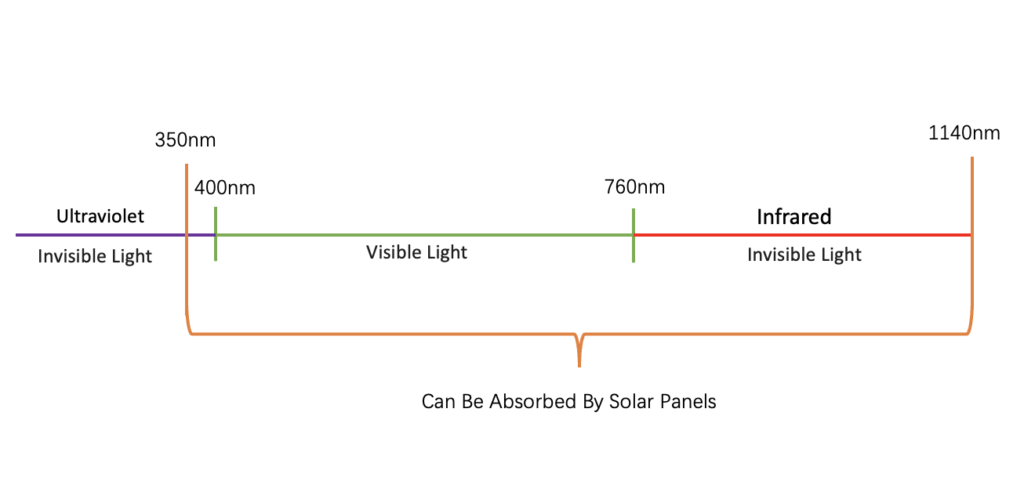
In fact, the solar spectrum is divided into visible light and invisible light. The wavelength of visible light is 400~760nm. Invisible light is divided into two types: the one located outside the red light is called infrared, with a wavelength greater than 760nm, up to 5300nm; the one located outside the purple light is called ultraviolet, with a wavelength of 290~400nm.
After repeated tests by scientists, only light with a wavelength of 350-1140nm is absorbed by the middle layer of the solar cell. This wavelength range includes the entire visible spectrum, a small amount of ultraviolet rays and a small amount of infrared rays. Therefore, the remaining ultraviolet light has a very short wavelength and can only stay on the surface. The remaining infrared light has a very long wavelength and will pass directly through the solar cell and cannot be absorbed.
What Is The Difference Between Artificial Light And Sunlight?
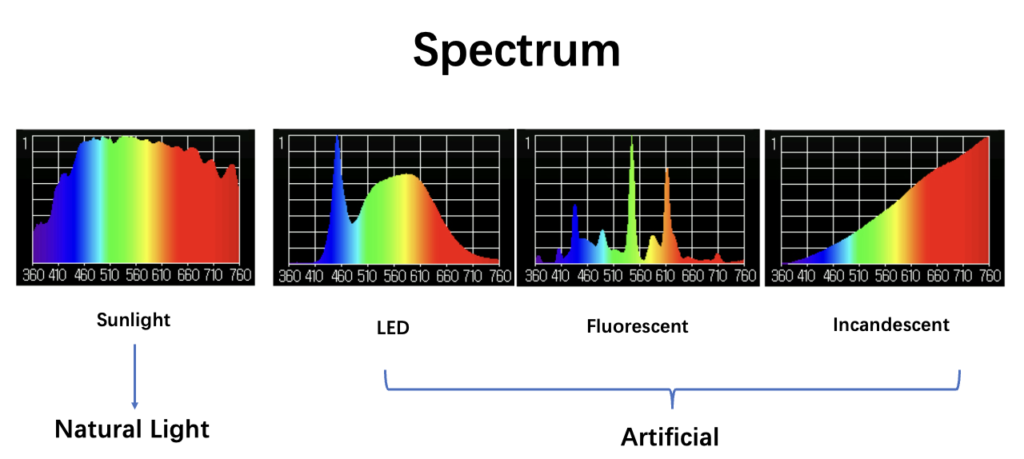
The solar spectrum is a continuous spectrum emitted by the sun. It contains light of various wavelengths from ultraviolet to infrared, and the spectrum is continuous without interruption or missing.
In contrast, the spectrum of artificial light sources varies due to different luminescence principles. For example, the spectrum of a linear light source such as a mercury lamp is relatively single and mainly consists of light of a specific wavelength, usually purple. LED light sources produce white light by mixing red, green and blue or using phosphors. The spectrum of such LED light sources is usually not continuous, but concentrated in certain wavelength ranges.
In addition, in terms of color rendering, sunlight contains the entire visible light spectrum, so it can accurately represent the original color of materials. Some artificial light sources may not be able to fully restore certain colors, causing objects to appear different in color under these light sources than under sunlight.
Why Do Light Photons Move Electrons Inside Solar Panels?
Light allows electrons in solar panels to move because of the photoelectric effect between light and electrons. The photoelectric effect is a physical process. When light shines on the surface of a solar panel, the electrons on the surface of the solar panel generate charges by absorbing photon energy.
As we just mentioned, the surface of the solar panel is made of semiconductor materials such as silicon. When sunlight shines on the solar panel, photons interact with atoms or molecules on the surface of the semiconductor material, and the energy of the photons is transferred to the electrons in semiconductor materials cause the energy level of the electrons to increase. When the energy of these electrons reaches a certain level, they can dissociate from the solid to form free electrons and positive ions. These free electrons are able to move freely within the solar panel’s circuit, creating an electrical current.
So can photons of artificial light move electrons in semiconductors? The answer is yes, but because there is a significant difference between the photons in artificial light and the photons in natural light, the effect of charging solar panels through artificial light will be very poor.
What Is The Difference In Photons In Sunlight And Artificial Light?
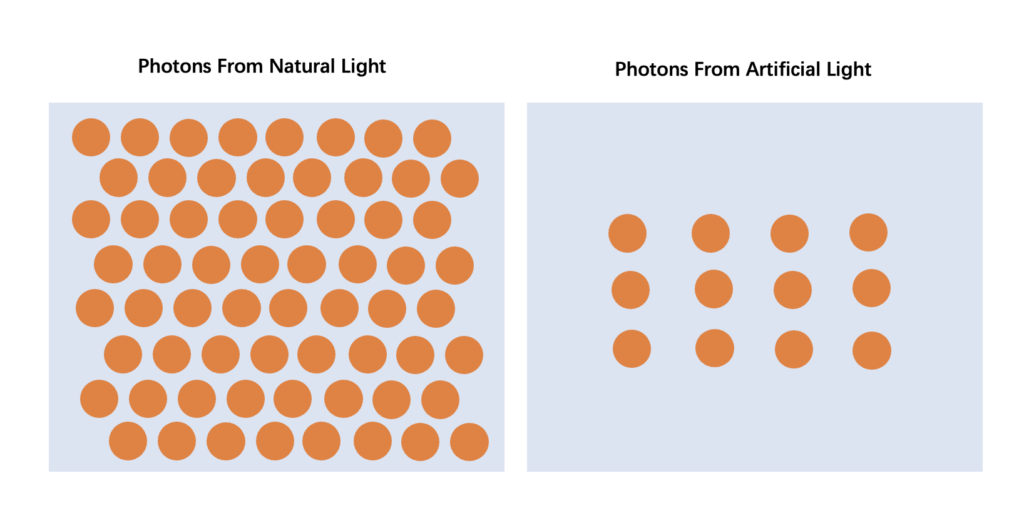
Sunlight is a natural light source with extremely high radiation power. The number of photons it emits per second is extremely large, so the radiation energy per second is also very huge. In addition, the solar spectrum contains various types of light from ultraviolet to infrared. The wavelength of light makes the distribution of photon energy relatively wide.
In contrast, the radiant power of artificial light sources is usually much lower because the spectrum of artificial light sources is mainly concentrated in certain wavelength ranges. This means that the number of photons emitted by artificial light sources is not only smaller overall, but also more narrowly distributed within a specific wavelength range.
So, overall, there are far more photons in sunlight than in artificial light sources. This explains why solar panels charge more efficiently outdoors in full sunlight, as sunlight provides more photons to activate electrons in photovoltaic cells.

Conclusion
Having said this, I believe everyone is already clear. Based on the working principle of solar panels, what is needed is sufficient and widely distributed photons in the solar spectrum to maximize the formation of current through the photoelectric effect. However, current artificial light sources cannot meet the requirements of sunlight conditions, therefore, it is very hard to use artificial light sources to charge solar panels.
Related Blogs
February 12, 2025
November 10, 2024
Share Via:
Get in Touch with Us Now!
Got questions or feedback? We’d love to hear from you! Just fill out the form below, and our friendly team will respond ASAP.
